Modeling
Modeling is a part of the definition phase of the Boomi DataHub lifecycle. Before managing master data, you must create data models. Models represent the structure and relationships of golden records (master data records).
Model fields represent meaningful business data that stays uniform and consistent over time. Models help you specify what fields you want to manage and how to manage them. They contain instructions that identify data that does not adhere to your model and data quality standards.
Model Components
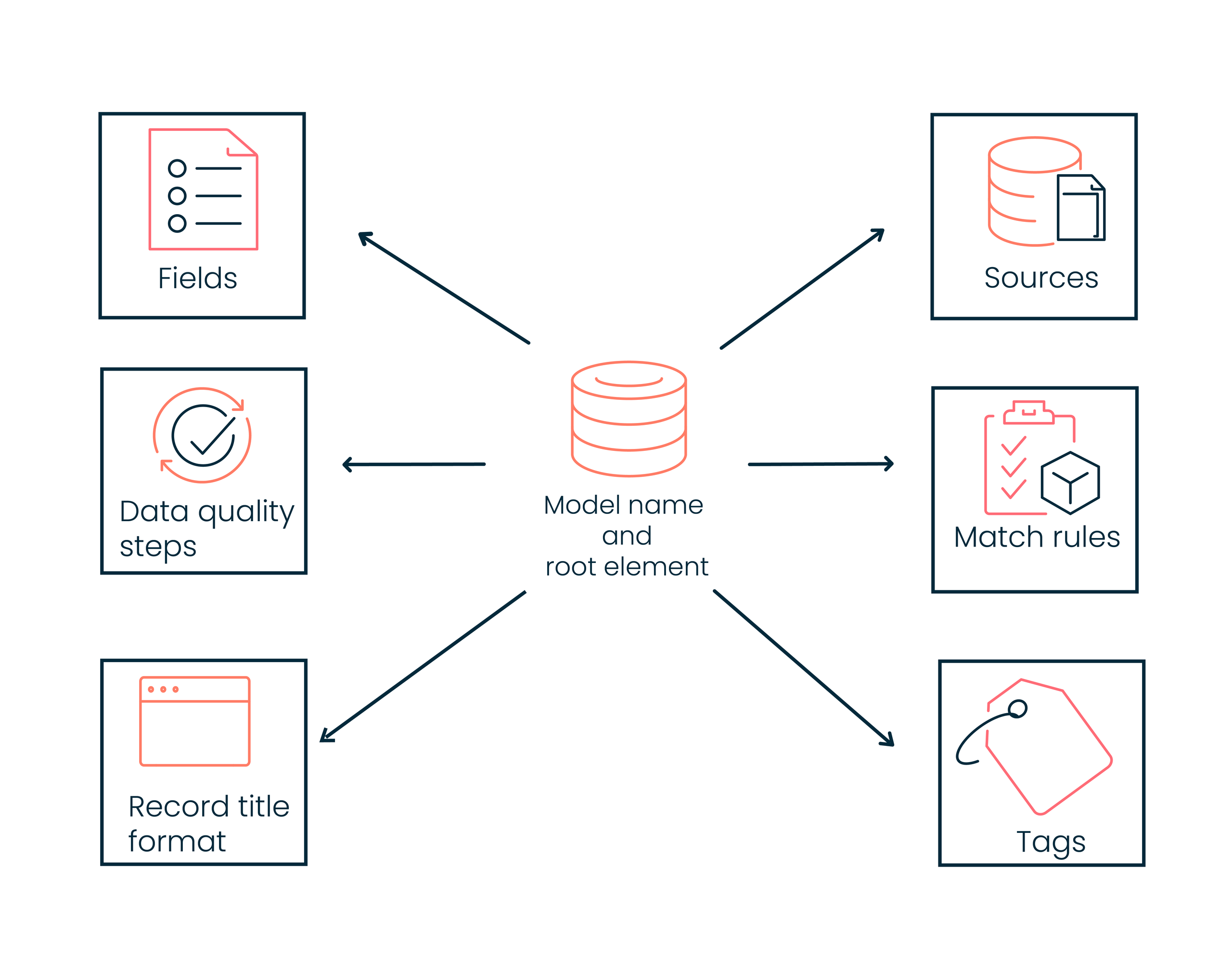
Models consist of the following components:
-
Name and Root Element - The model name also serves as the domain name once the model is deployed. It must contain at least one letter and allows a maximum length of 255 characters. The Root Element Name is derived from the specified model name and is the name of the required root XML element in batches of source entities contributed to the domain after deployment of the model.
-
Fields - Fields are data categories for a specific area of focus. They describe the contents of a golden record. For example, the first name, last name, street address, and state fields for a customer contact record.
-
Sources (recommended) - You can attach source settings to a model, which indicates how sources interact with the repository. This is beneficial in scenarios where you use the same settings every time you deploy the model. For example, you attach source settings because every time you deploy the model, MySQL will always contribute data.
-
Data quality steps (recommended) - Data quality steps improve and/or validate data from incoming sources to ensure accuracy. They protect the quality of master data. You can use business rules and design flexible integrations that enrich data from third-party services, such as Loqate. For example, you can create custom criteria in business rules to quarantine records with missing area codes in phone numbers.
-
Match rules - Match rules are an essential part of data models. They identify unique and duplicate incoming data. They help Boomi DataHub know when to update field values in an existing record and when to create a new record. A data model can have multiple match rules.
-
Record Title Format (optional) - Record titles help you quickly identify golden records and steward data. You can customize golden record titles using up to three field values. For example, you can specify that a golden record’s title contains the last name then first name.
-
Tags (optional) - Tags categorize golden records based on rules about field data. They are used to classify golden records for governance purposes. For example, you can apply a “customer” tag to distinguish customer records from prospective customers and partners. Golden records can have multiple tags.
Designing and Creating Models
To simplify and streamline model creation you can:
-
Import a file containing fields from a source system, such as Salesforce.
-
Use Boomi Suggest to select the most popular fields used by other Boomi Community members for a specific domain, such as Customer Contact.
-
Copy an existing model.
You always have the option to add fields manually to achieve your data management goals. You can create models in the user interface or you can use the Create Model endpoint in the Hub Platform API.
Boomi Suggest
Boomi Suggest analyzes models across the Boomi Community to intelligently suggest the most popular fields for a specific domain. You can use Boomi Suggest to provide field suggestions and to provide insight about how your fields compare with peers in the community.
Suggestions are available for the following domains: Account, Customer, Employee, Location, Product, and Vendor. Field recommendations are divided into three categories: High Confidence, Medium Confidence, and Low Confidence, meaning the popularity of the field among the community.
Data Masking
You can configure model fields with the following options so that field values with sensitive data are masked.
- All - hides entire data. Displays all field values as five asteriks. Available for all data types except Reference.
- Partial Mask - hides a portion of the data. Not available for Boolean and Reference type fields.
- Partial Show - reveals a portion of the data. Not available for Boolean and Reference type fields.
- None - reveals entire data
You must have one of the following user permissions to view masked data:
- MDM - Privileged Data Steward role
- MDM - Administrator role
- MDM - Reveal Masked Data privilege
- MDM - Data Steward role (or MDM - Stewardship privilege) and the Reveal Masked Data Hub entitlement (available with the Advanced Security feature)
Publishing Models and Model Versions
Models start as drafts. You must publish a model before you can deploy it to a repository. Boomi DataHub applies a version number to a published model and saves its history. You can create multiple versions of models. In the Models page or Repositories page, you can deploy a previous version or later version of a model.
Testing Models and Staging Data
Staging your data helps you preview the incorporation of data into master records without the risk of sending invalid data to source systems. After you create and deploy a model to your development and test repository, test your model’s matching rules to see if your model design achieves your desired results for master data management and data synchronization.
You can edit your model and deploy a new model version to a repository to make adjustments until you are satisfied with the golden records for the domain and the flow of data.
Sharing Models
If you have multiple Boomi accounts, you can share models among your accounts. This is useful for Boomi partners who want to share models with their customer accounts. Customers can use shared models as templates. Read Sharing a model with an account group to learn more about account groups.
